By using virtual modules we can guide learners through step-by-step maintenance procedures for different fluid power components and systems, ensuring they understand best practices for upkeep and minimizing downtime in real-world applications.

Engineers and designers can use VR to visualize and manipulate 3D models of products in a virtual environment. This enables them to assess designs, identify potential issues, and make improvements before physical prototypes are built, reducing development time and costs.
VR enables remote experts to provide real-time guidance and support to on-site technicians. Using VR headsets or augmented reality (AR) glasses, technicians can receive visual instructions, annotations, and virtual overlays, improving troubleshooting and maintenance efficiency.
VR can assist in designing and optimizing factory layouts by creating virtual representations of production facilities. Manufacturers can assess different layout options, evaluate space utilization, and visualize workflows to optimize resource allocation and minimize logistical challenges.
VR simulations can recreate hazardous scenarios and environments, allowing workers to undergo safety training without exposing them to real risks. Employees can learn to recognize and respond to safety hazards in a controlled virtual setting, enhancing workplace safety practices.
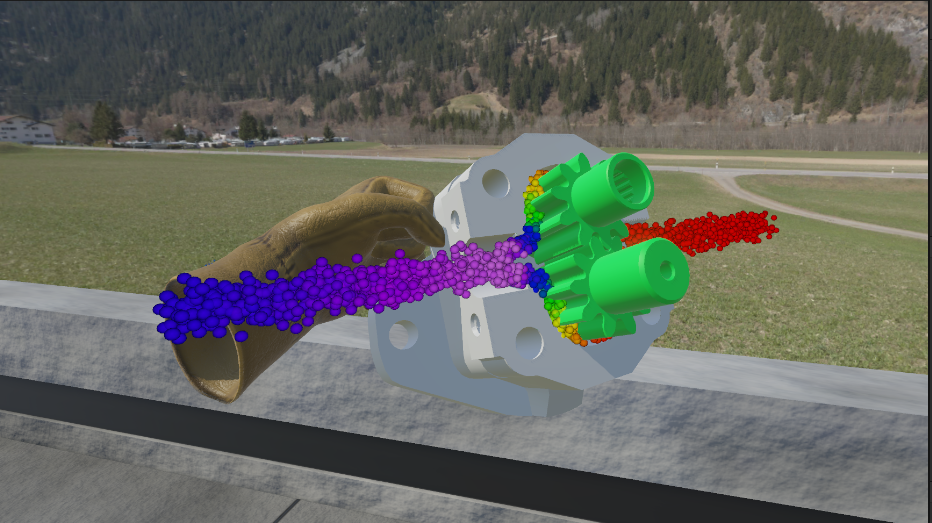
Simulate the operation of various fluid power equipment, allowing learners to practice controlling hydraulic or pneumatic systems without the need for physical machinery, reducing costs and safety risks.
Virtual training platforms can present learners with realistic troubleshooting scenarios, where they can diagnose and rectify common issues in fluid power systems, enhancing their problem-solving skills in a controlled environment.
By using virtual modules we can guide learners through step-by-step maintenance procedures for different fluid power components and systems, ensuring they understand best practices for upkeep and minimizing downtime in real-world applications.
Our systems can track and assess learners’ performance in real-time, providing immediate feedback and personalized recommendations for improvement to enhance skill development and proficiency.

VR technology can be used to visualize potential hazards and assess risks in various work environments. Safety professionals can create virtual representations of workplaces, identify safety hazards, and evaluate their potential impact on workers’ health and safety.
VR simulations can provide hands-on training for operating machinery and equipment safely. Employees can practice using equipment controls, follow safety protocols, and learn proper handling techniques in a virtual environment.
Safety inspectors can use VR technology to conduct virtual inspections of facilities and worksites. VR-enabled inspections allow inspectors to remotely assess safety compliance, identify potential violations, and document findings without physically visiting the site.
VR allows for realistic simulations of emergency scenarios, such as natural disasters, chemical spills, or medical emergencies. Emergency responders can train in virtual environments to improve their response times, decision-making skills, and coordination during crisis situations.

By placing students in realistic simulations or virtual worlds, VR allows them to experience concepts firsthand, making learning more memorable and engaging.
Educators can create custom VR modules that adapt to students’ learning styles, pace, and proficiency levels, providing targeted instruction and feedback.
Virtual environments can be designed to accommodate different learning styles, sensory preferences, and accessibility requirements, ensuring that all students have equal opportunities to participate and succeed.
Students can engage in hands-on activities, simulations, and virtual labs that replicate real-world scenarios, allowing them to apply theoretical concepts in a practical context.
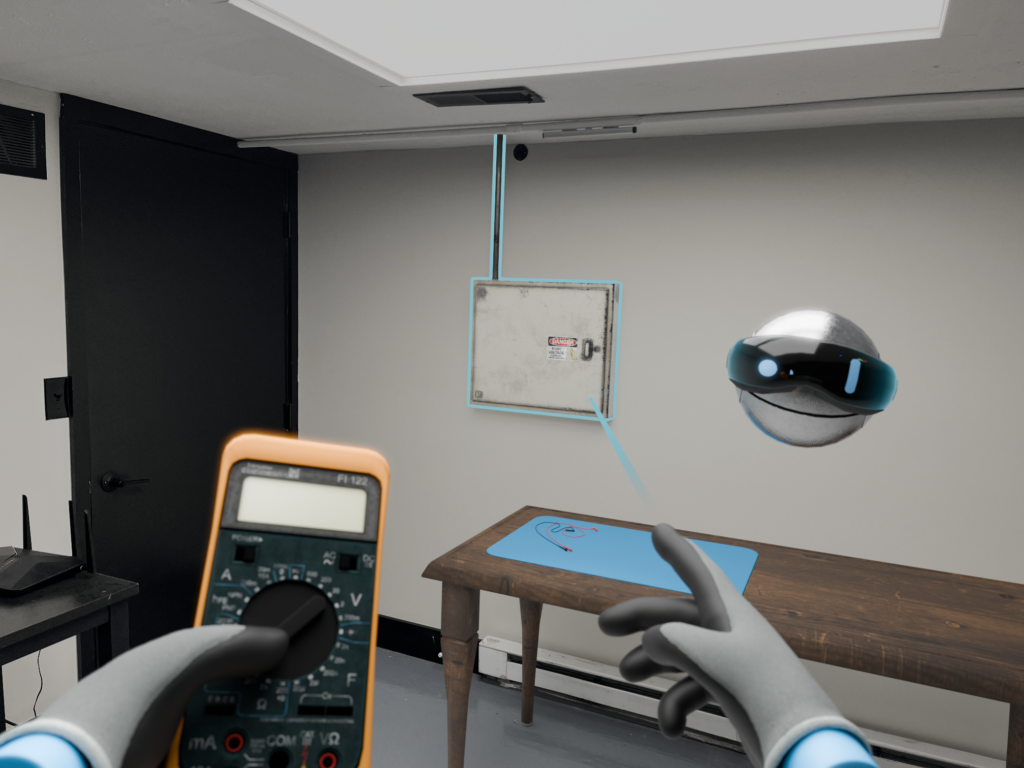

Simulate hazardous scenarios, allowing learners to practice safety protocols, such as working with high voltage equipment, in a risk-free environment.
Virtual simulations can replicate the operation of electrical equipment, enabling learners to practice tasks like circuit troubleshooting, panel installation, and maintenance procedures without the need for physical hardware.
Educate your students on electrical codes and regulations, providing interactive scenarios to reinforce understanding and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Empower your workforce to learn soft skills essential to the electrical industry, such as communication, teamwork, and project management, through simulated workplace environments and collaborative exercises.
© 2024 VR Acquisition Holdings, LLC